
Publication & Application notes


Robust Oligonucleotide Impurity Profiling in a GMP Setting Using the Waters SQ Detector 2 Mass Detector
This study presents a reliable and easy-to-implement method using the SQ Detector 2 Mass Detector and Empower™ Software for the routine impurity analysis of oligonucleotides in QC laboratories.

High-performance PK assay for biotherapeutic antibodies in dog serum: development and qualification with Gyrolab platform
Pharmacokinetic (PK) testing is essential for understanding the behaviour of a therapeutic drug within the body, which is crucial for determining its efficacy and safety. These assessments help define the appropriate dosage, route, and schedule of administration in preclinical an

Development of a Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR) assay for evaluating the allogenicity of cell therapy products
Cell therapies represent a promising class of treatments with the potential to address many incurable diseases through unique and powerful mechanisms of action. Despite recent successes, these therapies still encounter significant challenges that impede their widespread applicati
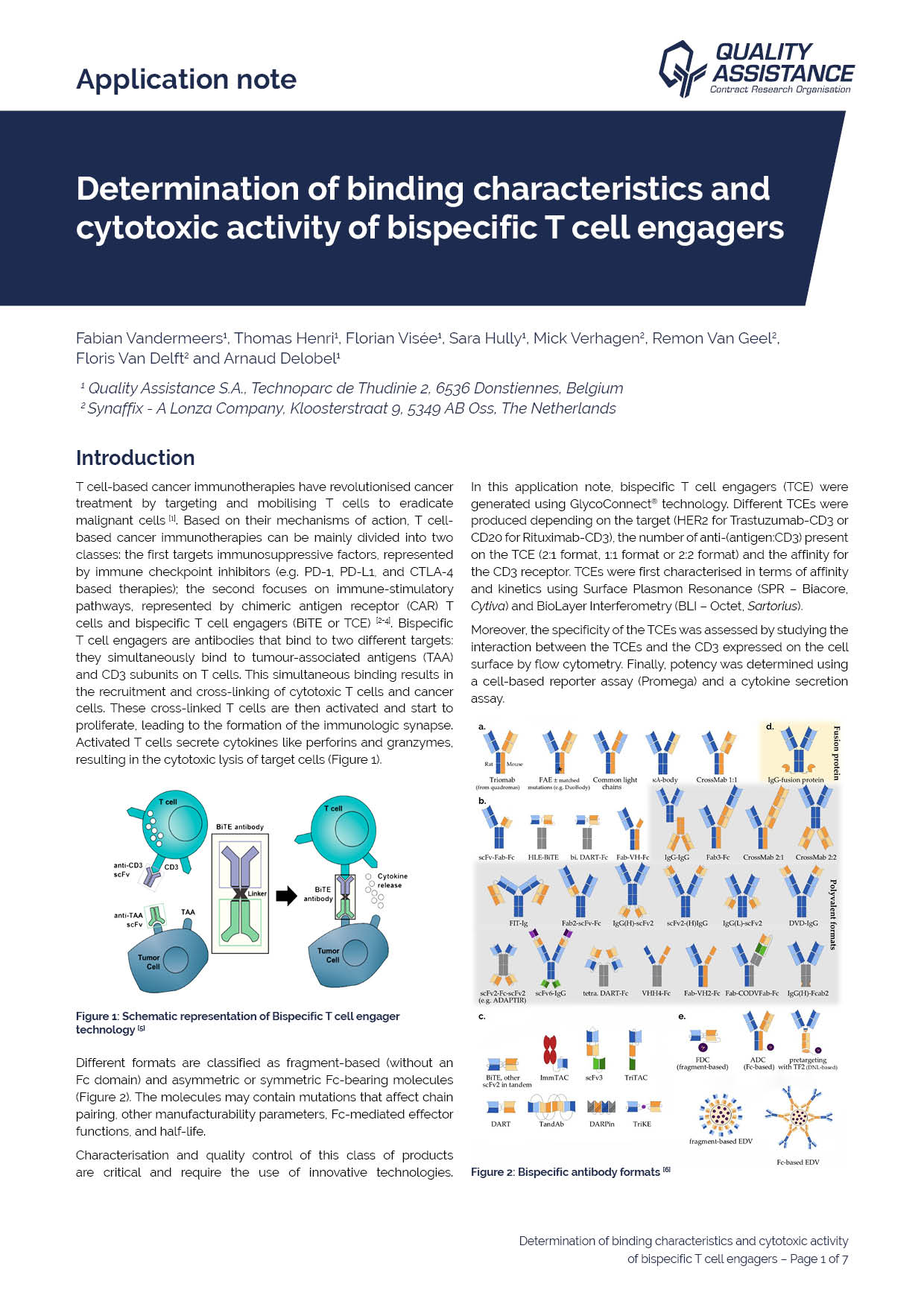
Determination of binding characteristics and cytotoxic activity of bispecific T cell engagers
1 Quality Assistance S.A., Technoparc de Thudinie 2, 6536 Donstiennes, Belgium
2 Synaffix - A Lonza Company, Kloosterstraat 9, 5349 AB Oss, The Netherlands
Advancing Gene Therapy: Enzyme Selection for Effective RNA Oligonucleotide Mapping
1 Quality Assistance
2 Waters Corporation

Comparison of 2 emulsion-based digital PCR systems: ddPCR from BioRad vs. dPCR from Stilla, for reliable determination of AAV genome titre
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) have emerged as a leading vector for gene delivery for treating various diseases due to its safety profile and efficient transduction of numerous

Recombinant Factor C method, benefits and validation
Pyrogenic substances in pharmaceutical products can induce life threatening fever reactions. Endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria were identified as the most prevalent and quantifiable pyrogens of concern.
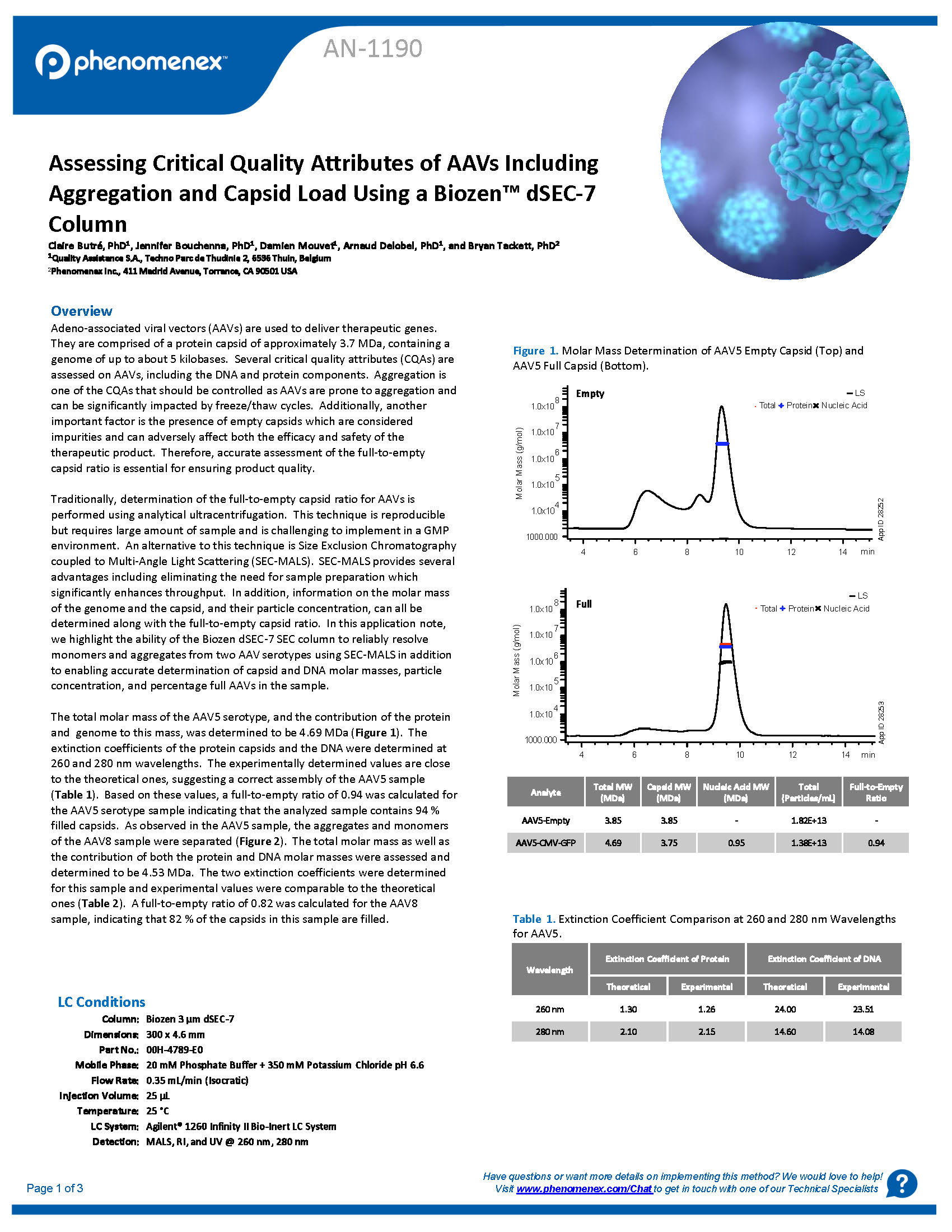
Assessing Critical Quality Attributes of AAVs Including Aggregation and Capsid Load Using a Biozen dSEC-7 Column
In this application note, we highlight the ability of the Biozen dSEC-7 SEC column to reliably resolve monomers and aggregates from two AAV serotypes using SEC-MALS in addition to enabling accurate determination of capsid and DNA molar masses, particle concentration, and percentage full AAVs in t
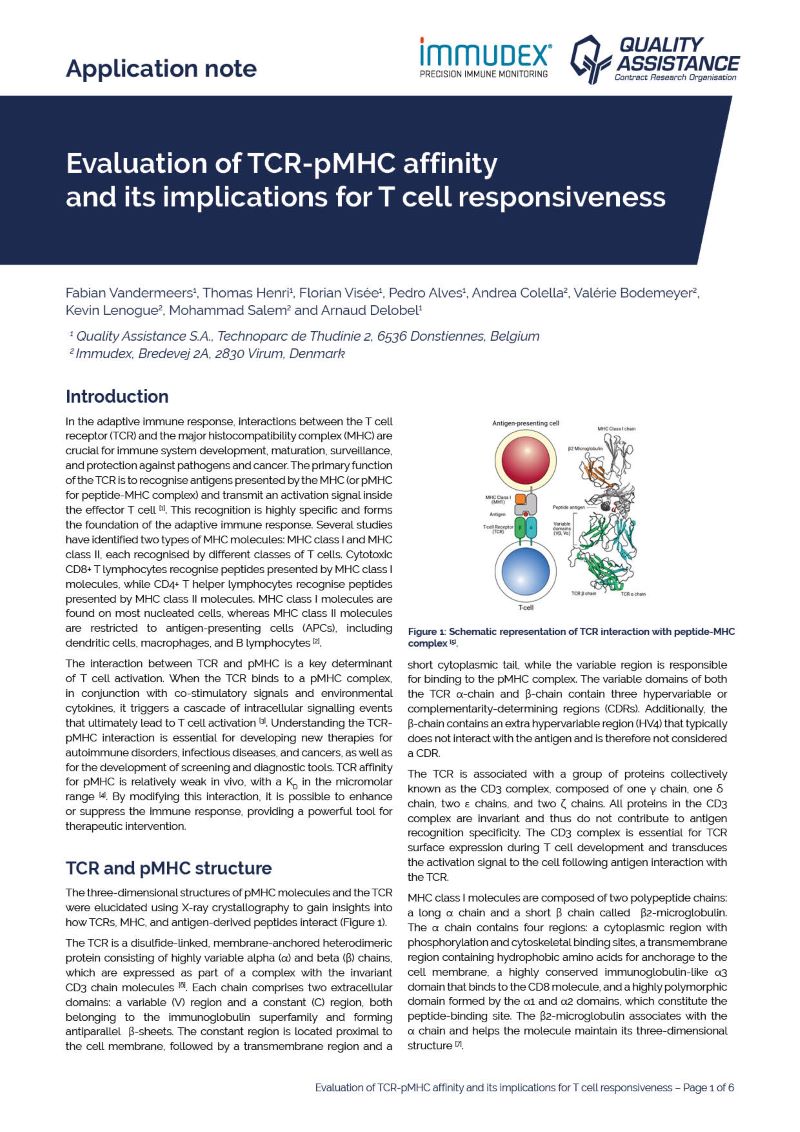
Evaluation of TCR-pMHC affinity and its implications for T cell responsiveness
In the adaptive immune response, interactions between the T cell receptor (TCR) and the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are crucial for immune system development, maturation, surveillance, and protection against pathogens and cancer. The primary function of the TCR is to r

Robustness evaluation of weak anion exchange chromatography method for the purity analysis of therapeutic oligonucleotides
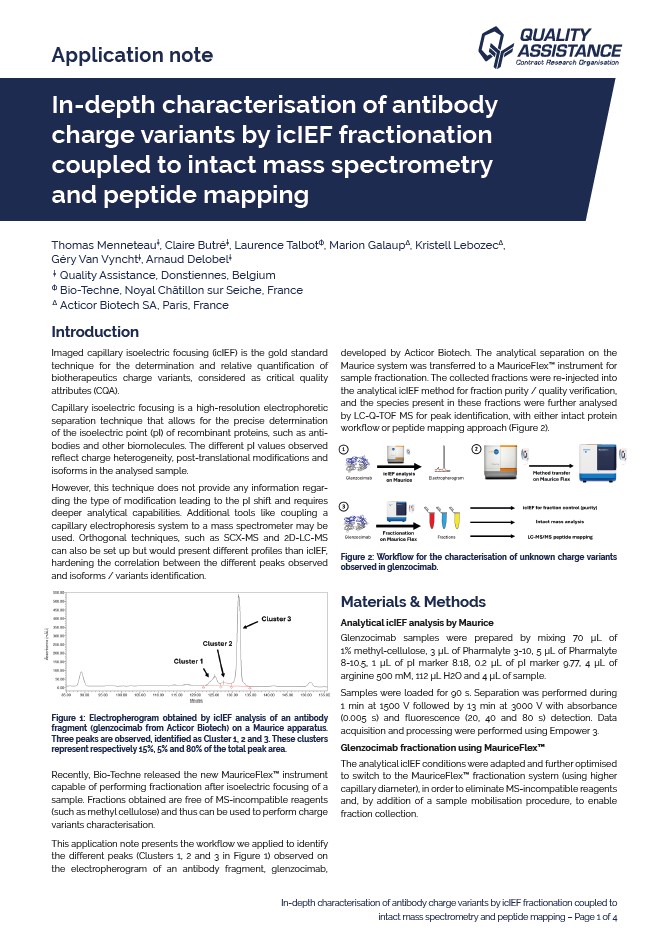
In-depth characterisation of antibody charge variants by icIEF fractionation coupled to intact mass spectrometry and peptide mapping
Imaged capillary isoelectric focusing (icIEF) is the gold standard technique for the determination and relative quantification of biotherapeutics charge variants, considered as a critical quality attributes (CQA).

Addressing common challenges of biotherapeutic protein peptide mapping using recombinant trypsin
Peptide mapping is the key method for characterization of primary structure of biotherapeutic proteins. This method relies on digestion of proteins into peptides that are then analyzed for amino acid sequence and posttranslational modifications.
Wide Pore Polymeric Reversed-Phase PLRP-S Columns for mRNA Analysis
Since the discovery of effective methods of delivery, messenger RNAs (mRNAs) have become increasingly popular in healthcare. These large, complex molecules are designed to allow cells to produce critical proteins and enzymes that can help fight disease.

Multi-Attribute Monitoring of Therapeutic mRNA by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Therapeutic mRNA is receiving growing interest in various therapeutic applications such as genome editing, cancer immunotherapy and prophylactic vaccines.

Alternative analytical solutions for endotoxin and pyrogen testing
At the cutting edge of analytical sciences, Quality Assistance is constantly investing in the latest technologies and equipment to provide the pharmaceutical industry with up-to-date services required by regulatory au

Assessment of Squalene-Adenosine Nanoparticles in Two Rodent Models of Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion
(1) Université Paris-Saclay, Institut Galien Paris-Saclay, CNRS UMR 8612, Pole Biologie-Pharmacie-Chimie, Bâtiment Henri Moissan, 6 Rue d’Arsonval, 91400 Orsay, France; rb.romain.brusini@gmail.com (R.B.)

Absolute quantification of proteins by ICP-MS/MS
Since 2015, Quality Assistance proposes to its partners a method based on Sulphur specific ICP-MS/MS detection combined with an 34S/32S isotope dilution quantification.

Characterisation of particle size distribution in Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors (AAVs) by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
Adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs) are small (~20-25 nm), non-enveloped viruses involved in the development of gene therapy protocols for the treatment of various diseases.

Analysis of Oligonucleotides by Size-Exclusion Chromatography: SEC-UV, SEC-MS, SEC-MALS
The field of therapeutic oligonucleotides has seen remarkable progress over the last years.
Implementation and development of OCTET Red96e BLI platform
Biologics (monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, etc.) are a class of complex molecules used in a wide range of therapeutic indications, including cancers and auto-immune diseases.

Interlaboratory Evaluation of a User-Friendly Benchtop Mass Spectrometer for Multiple-Attribute Monitoring Studies of a Monoclonal Antibody
(1) Quality Assistance sa, Technoparc de Thudinie 2, 6536 Thuin, Belgium
(2) School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Geneva, CMU—Rue Michel Servet 1, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland

New 2D-LC–MS Approaches for the Analysis of In-Process Samples and for the Characterisation of mAbs in a Regulated Environment
Biologics, and in particular monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), are an important class of therapeutics, and their market share keeps growing. The production of antibodies is a complex and lengthy process.
Validation of a Monocyte Activation Test (MAT) using the PyroMAT™ kit
Pyrogen testing is a regulatory requirement to ensure the product quality and safety of pharmaceutical products, as pyrogens can induce life threatening fever reactions.

Capillary isoelectric focusing (icIEF) bridging study between iCE3 and Maurice equipment
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) constitute a major and fast-growing biotherapeutic class, thanks notably to their outstanding selectivity for specific targets.

A new alternative tool to analyse glycosylation in pharmaceutical proteins based on infrared spectroscopy combined with nonlinear support vector regression
(a) University of Liege (ULiege), CIRM, Vibra-Sante Hub, Department of Pharmacy, Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry, Liege, Belgium

Quantification of residual CHO host cell DNA in biotherapeutics in-process samples using KingFisher Flex system
The presence of residual host cell DNA in biopharmaceutical products can induce severe side effects for patients.
Development and validation of an antibody-drug conjugate bioassay
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a class of drugs used in the treatment of different cancers. Unlike chemotherapy, ADCs are designed to only target and kill tumour cells. Structurally, ADCs are complex molecules composed of an antibody linked to a cytotoxic co
DryLab and Empower: a successful combination for the optimisation of mAb subunit analysis
The development of liquid chromatography (LC) methods has long been done using a trial-and-error approach, also known as “one factor at a time” (OFAT). While this approach is the easiest to implement, it is both time-consuming and quite inefficient.
Fast and accurate absolute quantification of antibodies and antibody-drug conjugate using Isotope Dilution-Triple Quadrupole ICP-MS
Traditional “absolute” methods of analysis for protein quantification include colorimetry, amino acid (AA) analysis and UV-Vis spectroscopy but each of these techniques has its limitations.
Development and validation of home-made Luminex assays for the quantification of multiple cytokines in human samples
Cytokine profiling is a powerful tool to link the host immune system with disease pathogenesis and/or treatment efficacy.
Development of orthogonal chromatographic methods for the purity analysis of therapeutic oligonucleotides
This application note presents the results obtained for the development of different HPLC methods on model therapeutic oligonucleotides, including R&D-grade Nusinersen, an approved 18-mer phosphorothioate oligonucleotide with 2’-O-(2-methoxyethyl) modifications.
Download the full document
Absolute Quantification of Oligonucleotides by ICP-MS/MS
A method was developed for the absolute quantification of purified therapeutic oligonucleotides, based on phosphorus determination by
ICP-MS/MS.
Download the full document
New 2D-LC/MS approaches for the analysis of in-process samples and for the characterisation of mAbs in a regulated environment
Two applications are presented here and describe the use of a 2D-LC system for MS characterisation of mAbs without sample preparation.
Download the full document
Charge variants analysis of monoclonal antibodies
Charge variants are considered as a Critical Quality Attribute of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, as they can have a significant impact on the efficacy of the drug. State-of-the-art analytical techniques are required to both quantify and identify the variants. In this application note, we present the portfolio proposed by Quality Assistance, including capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) and ion-exchange chromatography (IEX), with applications to commercial monoclonal antibodies. Approaches based on (2D-)LC/MS are presented for the identification of the variants.
Download the full document
Development, optimisation and validation of a TNFα neutralising assay using a Quality by Design approach
Using a QbD approach, we developed a TNFα neutralising assay capable of fulfilling the Analytical Target Profile. Statistical Design of Experiment was applied to evaluate the effect of the different factors and to choose the optimal parameters.
Download the full document
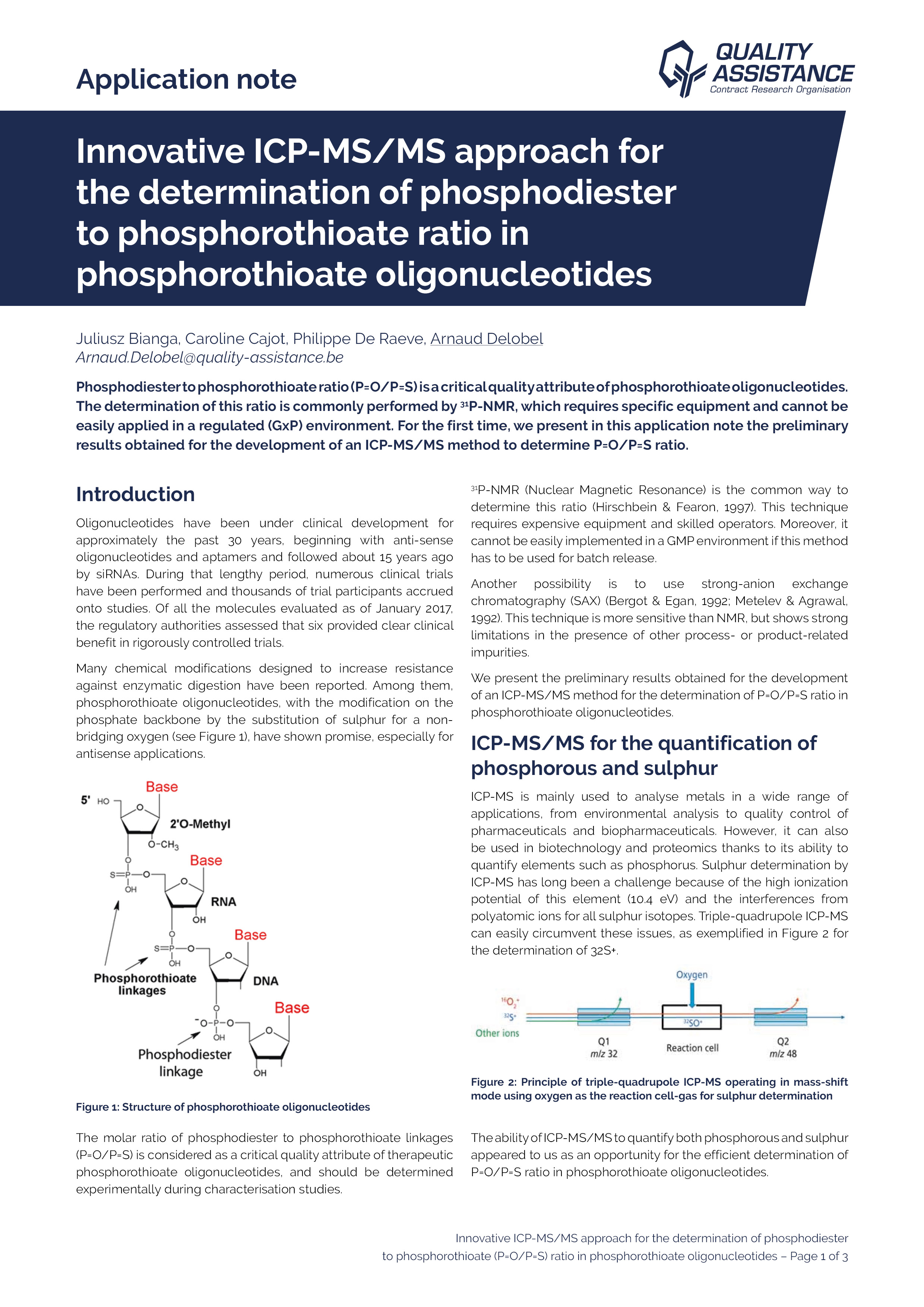
Innovative ICP-MS/MS approach for the determination of phosphodiester to phosphorothioate ratio in phosphorothioate oligonucleotides
Phosphodiester to phosphorothioate ratio (P=O/P=S) is a critical quality attribute of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. The determination of this ratio is commonly performed by P-NMR, which requires specific equipment and cannot be easily applied in a regulated (GxP) environment. For the first time, we present in this application note the preliminary results obtained for the development of an ICP-MS/MS method to determine P=O/P=S ratio.
Download the full document

Stress testing of Humira (adalimumab) monitored by Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX-MS)
In this application note, we present how this technology can be used to monitor structural changes at the amino acid level during stress testing studies of a monoclonal antibody. This appreach can be applied similarly to stability studies.
Download the full document

Epitope mapping of an interleukin receptor for three therapeutic antibodies by Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX-MS)
In this application note, we present a case study in which we performed epitope mapping for three monoclonal antibodies binding to an interleukin receptor.
Download the full document

Analytical Characterisation of Cell-Based Medicinal Products
Ensuring the characterisation of in vitro differentiated cells for therapeutic purposes brings many challenges. These include the difficulty of controlling cell variability and complexity of the steps required to generate a stable product.
Download the full document
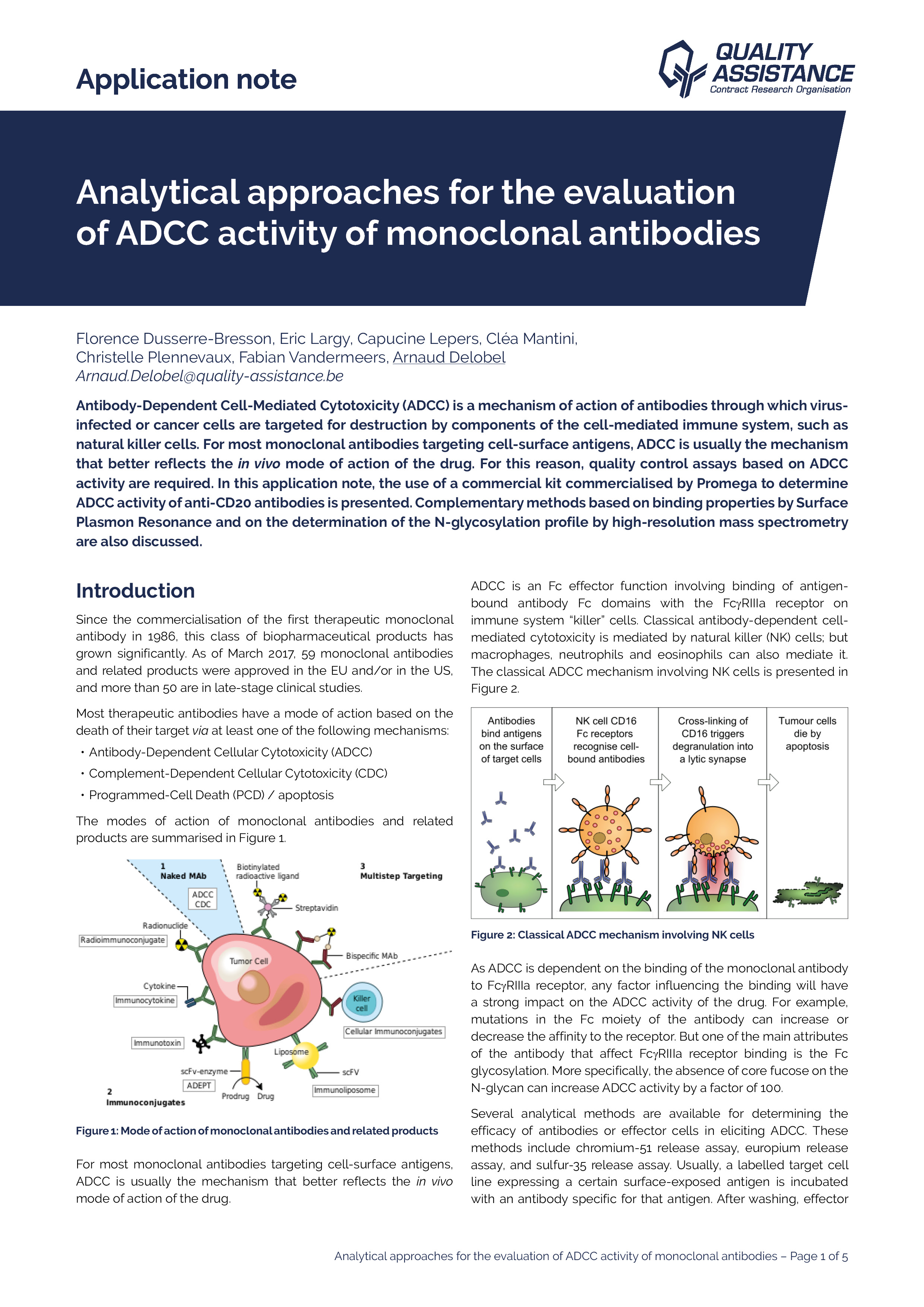
Analytical approaches for the evaluation of ADCC activity of mAbs
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) is amechanism of action of antibodies through which virus-infected or cancer cells are targeted for destruction by components of the cell-mediated immune system, such as natural killer cells.
Download the full document
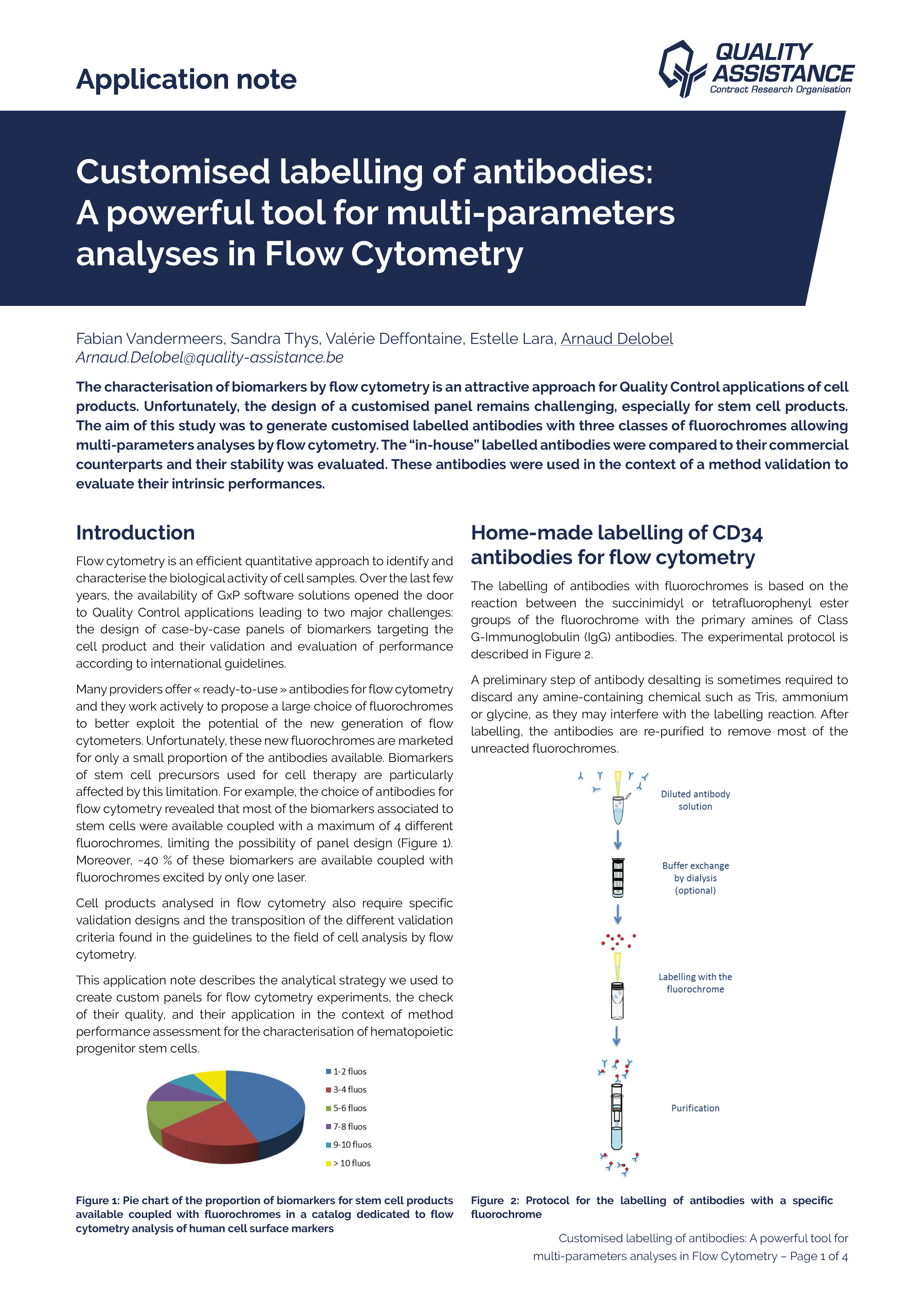
Customised labelling of antibodies: A powerful tool for multi-parameters analyses in Flow Cytometry
The characterisation of biomarkers by flow cytometry is an attractive approach for Quality Control applications of cell products. Unfortunately, the design of a customised panel remains challenging, especially for stem cell products.
Download the full document

Characterisation of the glycosylation of Humira (adalimumab) and Erbitux (Cetuximab) by high resolution mass spectrometry
Due to their mode of production, therapeutic mAbs present diverse and heterogeneous glycosylations. Their analysis may require the use of orthogonal techniques in order to fully characterize their nature and location. In this application note, the use of mass spectrometry as a powerful tool for Adalimumab and Cetuximab glycosylation characterization is presented.
Download the full document

Characterisation of Anti-HCP antibodies by 2D differential Gel Electrophoresis
Host-cell proteins are a major class of process-related impurities in biotherapeutics that can impact the safety and efficacy of the product. Despite the advent of advanced analytical techniques, ELISA remains as the industry gold standard for the detection and quantification of HCPs during process development and for routine analyses.
Download the full document
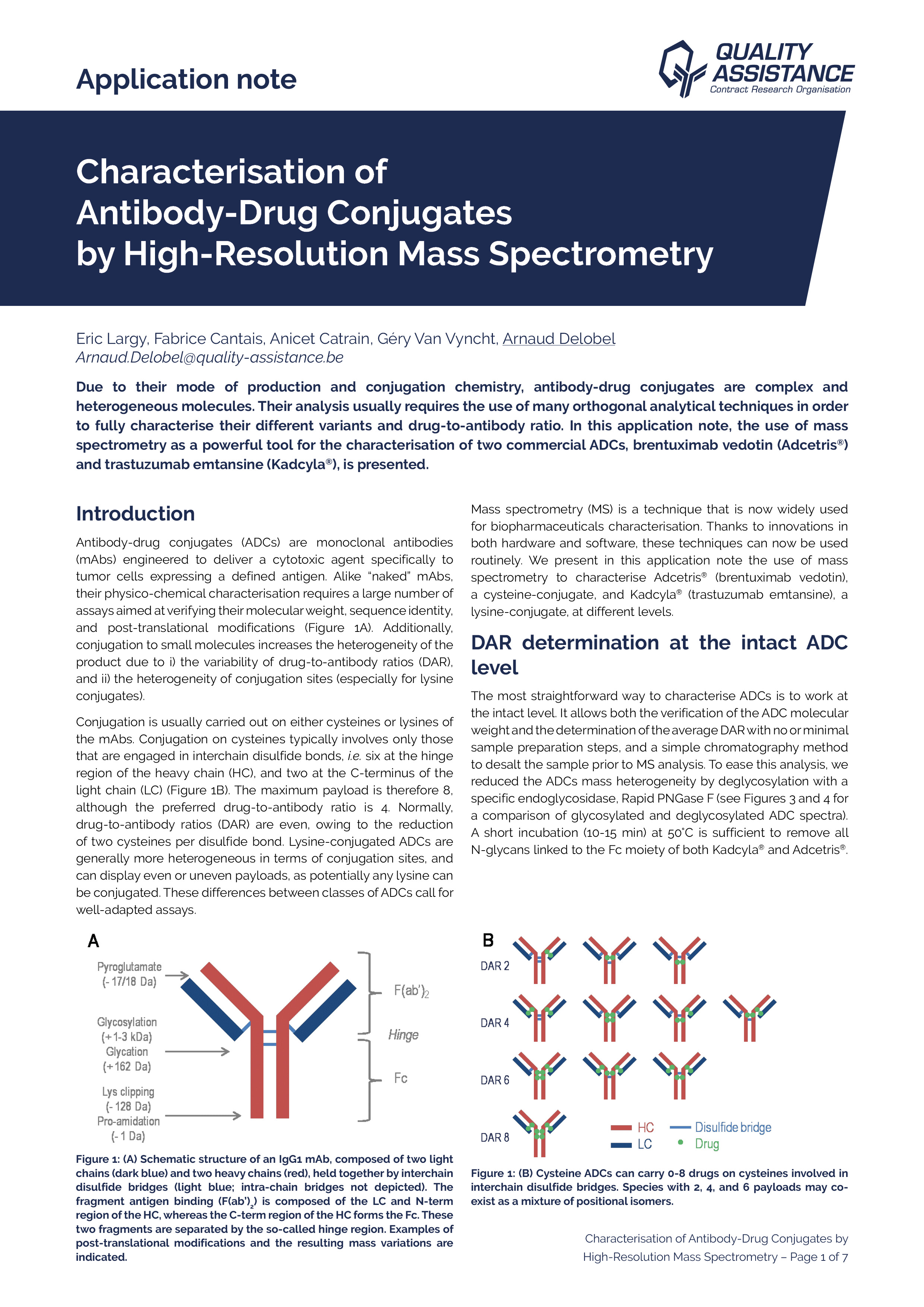
Characterisation of Antibody-Drug Conjugates by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Due to their mode of production and conjugation chemistry, antibody-drug conjugates are complex and heterogeneous molecules. Their analysis usually requires the use of many orthogonal analytical techniques in order to fully characterise their different variants and drug-to-antibody ratio.
Download the full document

Characterisation of the glycosylation of Enbrel: Etanercept by high resolution mass spectrometry
Due to their mode of production, therapeutic glycoproteins present complex and heterogeneous glycosylations. Their analysis usually requires the use of many orthogonal analytical techniques in order to fully characterise their nature and location.
Download the full document
Human platelet lysate as additive for Wharton's Jelly-MSC culture
This application note presents the results obtained during a study performed to evaluate the use of human Platelet Lysates (hPL) as an alternative to Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) in culture media for Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC)
Download the full document

Surface Plasmon Resonance
Biotherapeutics are a class of complex molecules that require the use of innovative techniques for their characterisation. Biacore technology offers label-free assays that provide precise and reliable concentration and kinetic measurements.
Download the full document
Characterisation of Humira Adalimumab by high resolution mass spectrometry
Due to their mode of production, monoclonal antibodies are complex and heterogeneous molecules. Their analysis usually requires the use of many orthogonal analytical techniques in order to fully characterise the different variants.
Download the full document
Fast and accurate absolute-quantification of proteins and antibodies using Isotope Dilution-Triple Quadrupole ICP-MS
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is used increasingly in metallomic studies to analyze metals and metal species and their interactions within biological and ecological systems.
Download the full document